GitLab Component
The Plumber GitLab Component lets you add compliance scanning directly to your GitLab CI/CD pipelines with a single line of configuration.
View on GitLabQuick Start (GitLab.com)
Info
These instructions are for projects hosted on gitlab.com. For self-hosted GitLab instances, see Self-Hosted GitLab below.
Create a GitLab token
In GitLab, go to User Settings → Access Tokens (or create one here) and create a Personal Access Token with
read_api+read_repositoryscopes.Add the token to your project
Go to your project’s Settings → CI/CD → Variables and add the token as
GITLAB_TOKEN(masked recommended).Tip
You can also use a project or group access token if you prefer scoped permissions.
Add to your pipeline
Add this to your
.gitlab-ci.yml:include:- component: gitlab.com/getplumber/plumber/plumber@~latestRun your pipeline
Plumber will now run on every pipeline (default branch, tags, and open merge requests) and report compliance issues.
Tip
Everything is customizable — GitLab URL, branch, threshold, and more. See Customize below.
Self-Hosted GitLab
If you’re running a self-hosted GitLab instance, you’ll need to host your own copy of the component since gitlab.com components can’t be accessed from your instance.
Import the repository to your GitLab instance
Go to New Project → Import project → Repository by URL and use this URL:
https://gitlab.com/getplumber/plumber.git. Choose a group and project name (e.g.,infrastructure/plumber).Enable the CI/CD Catalog
In your imported project, go to Settings → General and make sure the project has a description (required for CI/CD Catalog). Then expand Visibility, project features, permissions, toggle CI/CD Catalog resource to enabled, and click Save changes.
Create a release
Go to Code → Tags and click New tag. Enter a version number (e.g.,
1.0.0) and click Create tag. The pipeline will create a release and publish the component to your instance’s CI/CD Catalog.Create a GitLab token
In the project you want to scan, go to User Settings → Access Tokens and create a Personal Access Token with
read_api+read_repositoryscopes. Then go to the project’s Settings → CI/CD → Variables and add the token asGITLAB_TOKEN(masked recommended).Tip
You can also use a project or group access token if you prefer scoped permissions.
Use the component in your pipelines
include:- component: gitlab.example.com/infrastructure/plumber/plumber@1.0.0The format is
<your-gitlab-host>/<project-path>/plumber@<tag>. Replace with your actual values.
If you prefer to build your own component, use templates/plumber.yml as a starting point.
See GitLab’s CI/CD component documentation for more details.
Compliance Controls
Plumber scans your GitLab CI/CD configuration and runs the following controls:
| Control | Description |
|---|---|
| Authorized image tags | Flags latest, dev, and other non-reproducible tags for container images used in CI/CD pipelines |
| Authorized image sources | Ensures container images used in your CI/CD pipelines come from approved sources |
| Branch protection | Verifies that repository branches are properly protected |
Info
More controls are coming soon. Check the GitHub releases for updates.
Customize
Override any input to fit your needs:
include: - component: gitlab.com/getplumber/plumber/plumber@~latest inputs: # Target (defaults to current project) server_url: https://gitlab.example.com # Self-hosted GitLab project_path: other-group/other-project # Analyze a different project branch: develop # Analyze a specific branch
# Compliance threshold: 80 # Minimum % to pass (default: 100) config_file: configs/my-plumber.yaml # Custom config path
# Output output_file: plumber-report.json # Export JSON report print_output: true # Print to stdout
# Job behavior stage: test # Run in a different stage allow_failure: true # Don't block pipeline on failure gitlab_token: $MY_CUSTOM_TOKEN # Different variable name verbose: true # Enable debug outputAll Inputs
| Input | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
server_url | $CI_SERVER_URL | GitLab instance URL |
project_path | $CI_PROJECT_PATH | Project to analyze |
branch | $CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME | Branch to analyze |
gitlab_token | $GITLAB_TOKEN | GitLab API token (requires read_api + read_repository scopes) |
threshold | 100 | Minimum compliance % to pass |
config_file | (auto-detect) | Path to config file (relative to repo root). Auto-detects .plumber.yaml in repo, falls back to default |
output_file | plumber-report.json | Path to write JSON results |
print_output | true | Print text output to stdout |
stage | .pre | Pipeline stage for the job |
image | getplumber/plumber:0.1 | Docker image to use |
allow_failure | false | Allow job to fail without blocking |
verbose | false | Enable debug output for troubleshooting |
Configuration
Plumber works out of the box with sensible defaults embedded in the image.
The component automatically detects your configuration using this priority:
config_fileinput set → Uses your specified path (relative to repo root).plumber.yamlin repo root → Uses your repo’s config file- No config found → Uses the default configuration embedded in the container
(Optional) Create a Configuration File
Option A: If you have the CLI installed (via Homebrew, Mise, or binary):
plumber generate configThis generates a default config file that you can customize.
Option B: Create manually based on the default config:
version: "1.0"
controls: imageMutable: enabled: true mutableTags: - latest - dev
imageUntrusted: enabled: true trustedUrls: - registry.gitlab.com/* - $CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE:*
branchProtection: enabled: true namePatterns: - main - release/*Tip
See the full configuration reference for all available options.
Example Output
Tip
The output is color-coded in your CI/CD job logs for easy scanning - green for passing controls, red for failures.
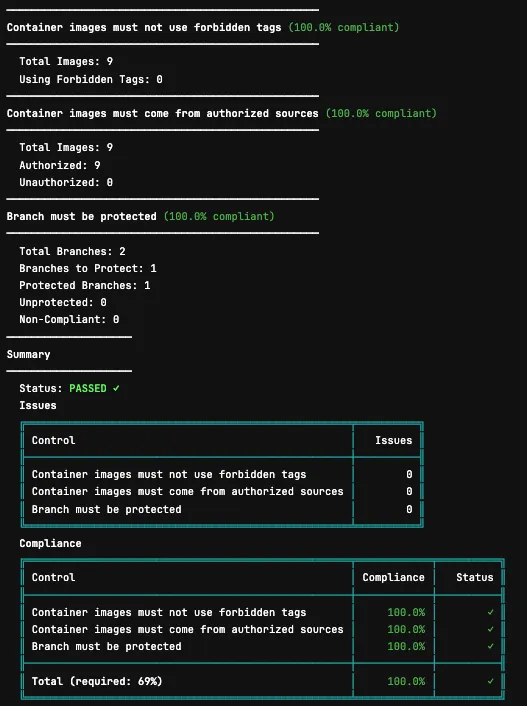
Troubleshooting
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
GITLAB_TOKEN environment variable is required | Add GITLAB_TOKEN in Settings → CI/CD → Variables |
401 Unauthorized | Check that your token has read_api + read_repository scopes |
403 Forbidden on MR settings | Expected on non-Premium GitLab; continues without that data |
| Component not found | For self-hosted GitLab, you must fork the component to your instance |