OpenSource CLI
The Plumber CLI allows you to analyze GitLab CI/CD pipelines from the command line. This is useful for local testing, CI/CD integration, or automated compliance checks.
View on GitHubInstallation
brew tap getplumber/plumberbrew install plumberInstall a specific version:
brew install getplumber/plumber/plumber@0.1.26Info
Versioned formulas are keg-only. Use the full path (e.g., /usr/local/opt/plumber@0.1.26/bin/plumber) or run brew link plumber@0.1.26 to add it to your PATH.
mise use -g github:getplumber/plumberInfo
Requires mise activation in your shell, or run with mise exec -- plumber.
Linux (amd64)
curl -LO https://github.com/getplumber/plumber/releases/latest/download/plumber-linux-amd64chmod +x plumber-linux-amd64sudo mv plumber-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/plumberLinux (arm64)
curl -LO https://github.com/getplumber/plumber/releases/latest/download/plumber-linux-arm64chmod +x plumber-linux-arm64sudo mv plumber-linux-arm64 /usr/local/bin/plumbermacOS (Apple Silicon)
curl -LO https://github.com/getplumber/plumber/releases/latest/download/plumber-darwin-arm64chmod +x plumber-darwin-arm64sudo mv plumber-darwin-arm64 /usr/local/bin/plumbermacOS (Intel)
curl -LO https://github.com/getplumber/plumber/releases/latest/download/plumber-darwin-amd64chmod +x plumber-darwin-amd64sudo mv plumber-darwin-amd64 /usr/local/bin/plumberWindows (PowerShell)
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri https://github.com/getplumber/plumber/releases/latest/download/plumber-windows-amd64.exe -OutFile plumber.exeVerify checksum (optional):
curl -LO https://github.com/getplumber/plumber/releases/latest/download/checksums.txtsha256sum -c checksums.txt --ignore-missingdocker pull getplumber/plumber:latestRun analysis directly with Docker:
docker run --rm \ -e GITLAB_TOKEN=glpat-xxxx \ getplumber/plumber:latest analyze \ --gitlab-url https://gitlab.com \ --project mygroup/myprojectgit clone https://github.com/getplumber/plumber.gitcd plumbermake build# or: make install (builds and copies to /usr/local/bin/)Info
Requires Go 1.24+ and Make.
Quick Start
Generate a config file
Terminal window plumber generate configThis creates
.plumber.yamlwith default compliance rules. You can customize it later.Create and set your GitLab token
In GitLab, go to User Settings → Access Tokens (direct link) and create a Personal Access Token with
read_api+read_repositoryscopes:Terminal window export GITLAB_TOKEN=glpat-xxxxTip
You can also use a project or group access token if you prefer scoped permissions.
Run analysis
Terminal window plumber analyze \--gitlab-url https://gitlab.com \--project mygroup/myprojectReview results
Plumber reads your
.plumber.yamlconfig and outputs a compliance report. You can also tell it to store the output in JSON format with the--outputflag.
Command Reference
plumber analyze
The main command for analyzing GitLab CI/CD pipelines.
plumber analyze [flags]Flags
| Flag | Required | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
--gitlab-url | Yes | - | GitLab instance URL (e.g., https://gitlab.com) |
--project | Yes | - | Project path (e.g., group/project) |
--config | No | .plumber.yaml | Path to configuration file |
--threshold | No | 100 | Minimum compliance % to pass (0-100) |
--branch | No | Project default | Branch to analyze |
--output | No | - | Write JSON results to file |
--print | No | true | Print text output to stdout |
Environment Variables
| Variable | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
GITLAB_TOKEN | Yes | GitLab API token with read_api and read_repository scopes |
Exit Codes
| Code | Meaning |
|---|---|
0 | Passed (compliance ≥ threshold) |
1 | Failed (compliance < threshold or error) |
plumber generate config
Generate a default .plumber.yaml configuration file.
plumber generate config [flags]| Flag | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
--output, -o | .plumber.yaml | Output file path |
--force, -f | false | Overwrite existing file |
Examples:
# Generate default configplumber generate config
# Custom filenameplumber generate config --output my-plumber.yaml
# Overwrite existing fileplumber generate config --forceUsage Examples
Save JSON Output
docker run --rm \ -e GITLAB_TOKEN=glpat-xxxx \ -v $(pwd):/output \ getplumber/plumber:latest analyze \ --gitlab-url https://gitlab.com \ --project mygroup/myproject \ --branch main \ --config /.plumber.yaml \ --threshold 100 \ --output /output/results.jsonSelf-Hosted GitLab
plumber analyze \ --gitlab-url https://gitlab.example.com \ --project mygroup/myproject \ --branch develop \ --config .plumber.yaml \ --threshold 80Silent Mode (JSON Only)
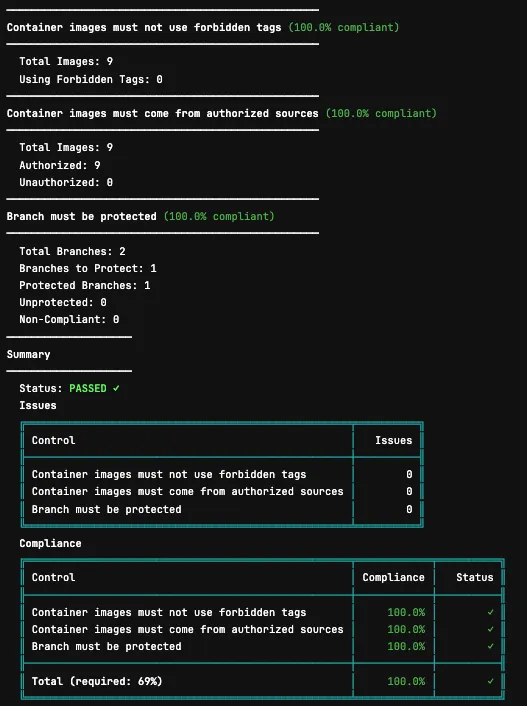
plumber analyze \ --gitlab-url https://gitlab.com \ --project mygroup/myproject \ --config .plumber.yaml \ --threshold 100 \ --output results.json \ --print falseExample Output
Tip
The CLI output is color-coded in your terminal for easy scanning - green for passing controls, red for failures.
Tip
When using --output, results are saved as JSON for programmatic access and CI/CD integration.
Configuration
Plumber uses a .plumber.yaml configuration file to customize checks.
Tip
See the Configuration section for full details.
version: "1.0"
controls: imageMutable: enabled: true mutableTags: - latest - dev
imageUntrusted: enabled: true trustDockerHubOfficialImages: true trustedUrls: - registry.gitlab.com/* - $CI_REGISTRY_IMAGE:*
branchProtection: enabled: true defaultMustBeProtected: true namePatterns: - main - release/*Troubleshooting
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
GITLAB_TOKEN environment variable is required | Set the GITLAB_TOKEN environment variable with a valid GitLab token |
401 Unauthorized | Check that your token has read_api + read_repository scopes |
403 Forbidden on MR settings | Expected on non-Premium GitLab; continues without that data |
404 Not Found | Verify the project path and GitLab URL are correct |
| Configuration file not found | Ensure the path to .plumber.yaml is correct (use absolute path in Docker) |